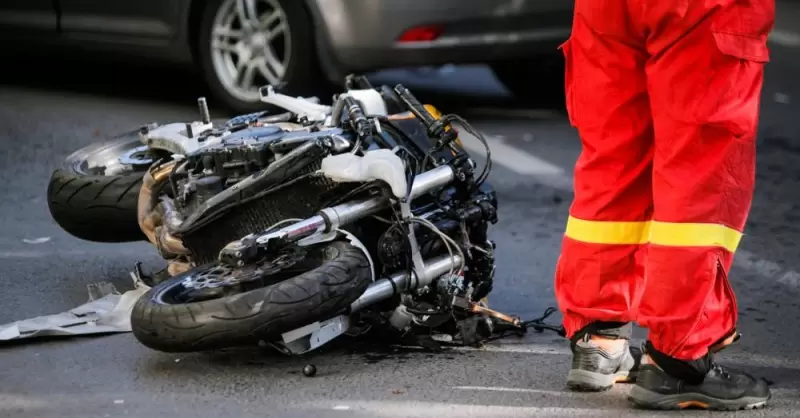
What Should You Do After a Motorcycle Accident in Atlanta, Georgia?

What Should You Do After a Motorcycle Accident in Atlanta, Georgia?

What Should You Do After a Motorcycle Accident in Atlanta, Georgia?
In Atlanta, Georgia, getting involved in a motorcycle accident can affect your health physically, financially, …

Automotive Industry: Approaches to Increase Security and Efficiency
Key Takeaways: Innovation in automotive manufacturing is crucial for efficiency and security. Technological advancements like …
Benefits and challenges of implementing workforce management software in modern businesses?
In the evolving business landscape, thriving in the competitive market and staying ahead can be …

A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Route Planning Software in Your Business
Introduction In a world where time is money and efficiency is the key to success, …

Claiming Your Rights With the Definitive Guide to Car Accident Claims
Roseville is a peaceful town in Placer County, California. While the locales are well-behaved and …

What Should You Do After a Motorcycle Accident in Atlanta, Georgia?
In Atlanta, Georgia, getting involved in a motorcycle accident can affect your health physically, financially, …
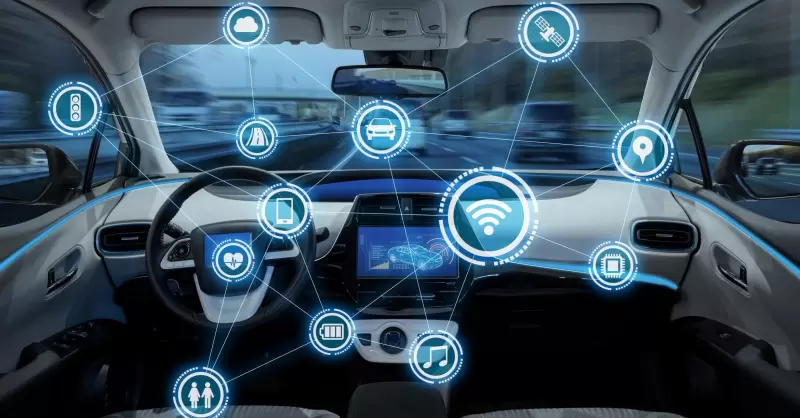

Automotive Industry: Approaches to Increase Security and Efficiency
Key Takeaways: Innovation in automotive manufacturing is crucial for efficiency and security. Technological advancements like …